SLAM and Reinforcement Learning in 3D environments
Introduction and Motivation
The idea for the project started from a very basic desire to use this time to learn more about SLAM and RL. After some research and reading papers about LSD Slam and ORB-Slam(or ORB slam), we formed the problem statement: How augmenting input features from SLAM affects the performance of RL in 3D environments? We each tried a different slam library pyslam, orbslam2 and orbslam3 and deep q learning architecture in the gym-miniworld 3d environment.
In the video, you can see one of the environments that we used in the gym-miniworld.
Why is this important?
We are looking into a future where a robot might be used to solve some challenging and difficult task without apriori knowledge about the environment. Very briefly explained SLAM has three important features: pose estimation, mapping in real-time and efficiently and planning where to go next. For the RL we have an agent that chooses actions and the environment to interact with. In this project we used a minimalist 3D RL environment with navigation based reward. The idea behind the solution is the assumption that SLAM will localize more efficiently than a DQN. However, one downside is the complexity of implementation for SLAM that slows it down.
Project Proposal
Midterm Report
Project code repo
https://github.com/balisujohn/766-final-project
Project Timeline
| When | Task |
|---|---|
| Before Feb 24 | Project Proposal and the initial webpage |
| Feb 25 - Mar 10 | Create DQN Miniworld benchmark |
| Mar 11- Mar 20 | Set up SLAM with Miniworld |
| Mar 21- Apr 6 | Design input encoding for SLAM features into |
| Apr 7 - Apr 21 | Contrast performance of DQN on Miniworld |
| Before May 5 | Complete project writeup and presentation |
Background
ORB-SLAM2
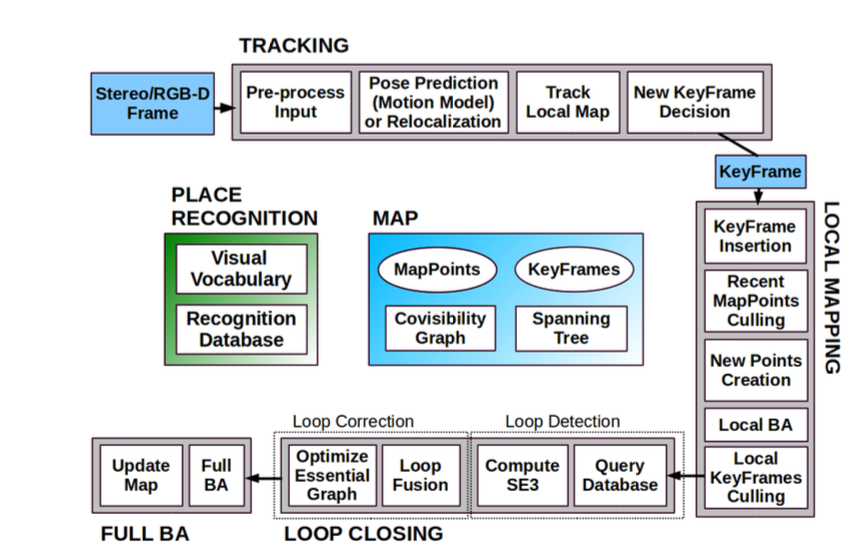
It is important to note that all of the ORB-SLAM algorithms use bundle adjustment(BA) to provide estimates of camera localization and sparse geometric reconstruction. Due to the lack of depth, we won’t be describing BA in detail. The tracking is the first step and it works by localizing the camera with every frame and deciding when to insert a new frame. The local mapping processes new keyframes and performs local BA. In this steep during tracking, culling of the points is applied to keep the high-quality points. The loop closing searches for the loops with every new keyframe. In the original ORB-SLAM, the final step is a pose graph optimization over similarity constraints to achieve global consistency. The final step of the loop closing when building a map, ORB-SLAM was built on the Essential Graph feature, which remains a part of the algorithm in all future versions. The system builds a spanning tree from the initial keyframe, and each time a new keyframe is inserted, it is included in the tree linked to the keyframe that shares most point observations. In a case when a keyframe is erased by culling, the system updates all the affected keyframesbags of words(BoW) place recognition module that performs loop detection and relocalization
Approach
In order to evaluate the relative performance of reinforcement learning with and without the inclusion of SLAM-derived features, we initially trained an agent to complete a modified version of the MiniWorld-Hallway-v0 environment.
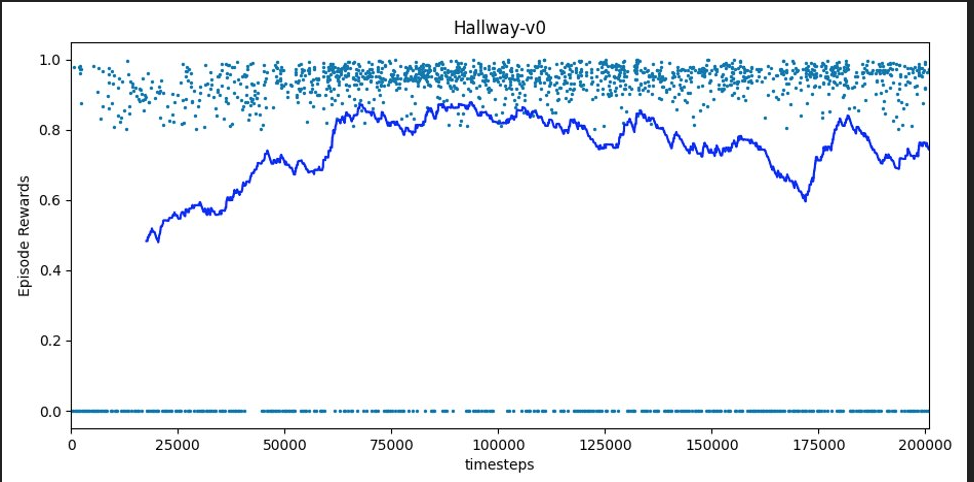
- Environment setting:
- Simulation environment: gym-miniworld
- SLAM library:
- pySLAM
- ORB-SLAM2 + python bindings
- ORB-SLAM3 (did not work well)
- Reinforcement learning library : Stable Baselines
ORB-SLAM2
It’s worth mentioning that most SLAM library are designed for ROS and C++ platform, such as orb-SLAM2 and lsd-SLAM, therefore we spent great effort in letting SLAM running on a python simulation environment without ROS.
- Modify step() function where each step action is defined in gym-miniworld so that it will call orb-slam2 directly
- Modify the python-binding for processMono() so that it will directly output 4x4 homogenous transformation matrix which contain position and orientation.
- Interpolate each action into 10 frames and feed into SLAM
- Camera calibration:
- OpenGL has some different way of defining the projection matrix and use angle of view to represent intrinsic camera information.
- Focal length:
-
Alpha = 2 arctan(d/2f)
where d is the dimension of image, alpha is the angle of view, f is the focus length.
- Principal points:
- camera set by gluperspective() function requires zero principle when map into normalized device coordinates(NDC), but since we export the rendering and fed that into SLAM as a OpenCV image, the principal points then becomes the center of image
PySLAM
In addition to Orb-SLAM 2, we used a modified version of pyslam to extract position and orientation. We reconfigured pyslam to accept an image as an argument and return the position and orientation quaternion. Pyslam also provides a monocular SLAM implementation, so it forms its localization and mapping estimates from a sequence of single-camera RGB images
ORB-SLAM3
ORB-SLAM3 is the latest in the ORB-SLAM libraries. There was a possibility that certain disadvantages of the other two libraries, like speed, and sudden map disruptions, would be resolved with ORB-SLAM3. After multiple attempts to make this work, and trying to modify some of the python bindings, we were unable to implement this approach.
However, we did do some background research how this library would work, so we provide a brief summary of some novelties and advantages.
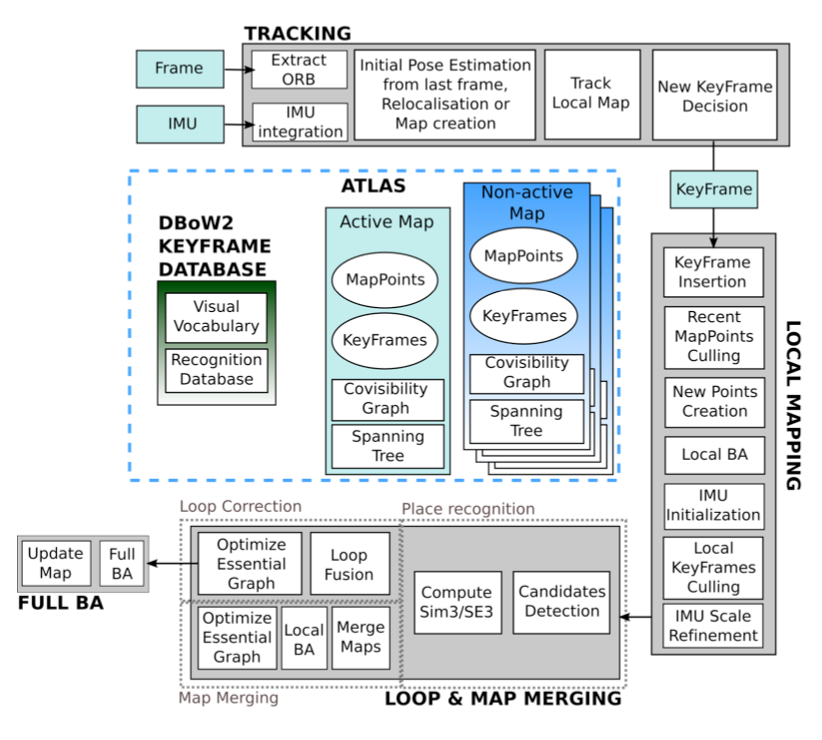
Atlas is a multi-map representation composed of a set of disconnected maps.
The tracking threadtakes input from the correct frame with respect to the active map in Atlas in real-time,
and it decided whether the currentframe becomes a keyframe.
If tracking is lost, the thread tries to relocate the current thread.
Depending on that, it decides whether the tracking is resumed, switching the active map if needed,
or whether or not the active map is storedas non-active, and a new map is initiated as an active map.
The next component is a local mapping thread that adds keyframes and points to the active map, removes the redundant ones,
and refines the map using visual or visual-inertialbundle adjustment.
Also, in the inertial case, the IMU parameters are initialized and refined by the mapping thread usingthe MAP-estimation technique.
The last component is the loop and map merging thread that detects common regions between the active map and the whole Atlas at keyframe rate.
The way this works is that the system checks whetherthe common area belongs to the active map.
The system then performs loop correction; if it belongs to a different map,both maps are seamlessly merged into a single one,
and this becomes a new active map.
Finally, a full BA runs as anindependent thread to prevent anything affecting a real-time map performance.
Results
ORB-SLAM2
Here is a demo video that pytorch is trying the agent with SLAM results in real-time.
Timing issue:
| Settings | Time per action |
|---|---|
| 10frames/action With viewer | 0.34s |
| 10frames/action Without viewer | 0.33s |
| 20frames/action | 0.67s |
| 5frames/action | 0.17s |
Resolution: 800x600
Problems to be solved:
1) speed, SLAM module will slow down the training speed
2) unexpected loop-closure & lost track: richness of texture inside simulation environment
PySLAM
We created a set of 200 reference images using our agent trained through standard DQN in modified MiniWorld-Hallway-v0 environment. We analyzed the time it took to perform SLAM on this sequence of images in pyslam
Future work
1) Encode the slam results into DQN model input
2) Improve the code performance to get faster performance
3) Find appropriate parameters that mitigate the “lost of track” issue